In the intricate tapestry of India’s administrative machinery, the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) stands as a cornerstone, guiding the nation’s recruitment processes and shaping the trajectory of its civil services. Established under the provisions of the Indian Constitution, the UPSC plays a pivotal role in selecting candidates for prestigious government positions, ranging from the coveted Indian Administrative Service (IAS) to various other central civil services.

According to Article 312 of the Indian Constitution, Parliament has the authority to establish one or more All India services, including an All India Judicial Service, applicable to both the Union and the States. Recruitment for these services is overseen by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC). At the state level, recruitment for administrative services is managed by the State Public Service Commission (SPSC).
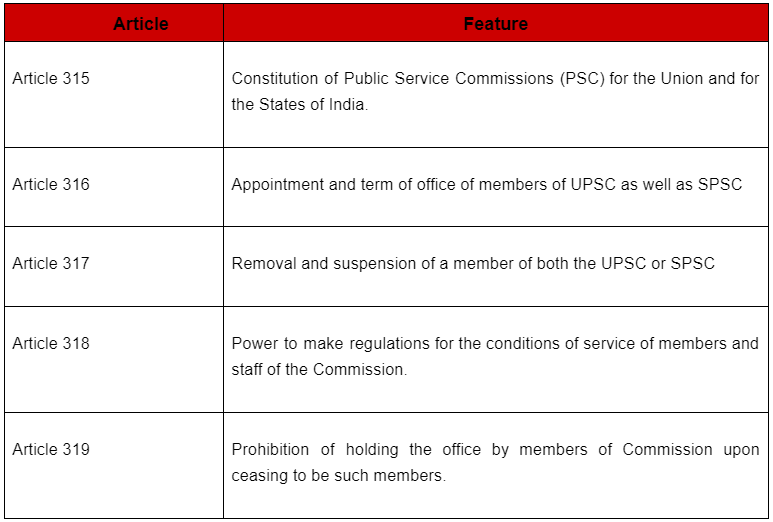
The UPSC serves as the central recruiting agency and operates independently as a constitutional body. The constitutional provisions regarding the composition, appointment, and removal of members, as well as the powers and functions of both the UPSC and SPSC, are outlined in Part XIV of the Indian Constitution, spanning from Article 315 to Article 323.
Constitutional Provisions
Composition of Union Public Service Commission
The appointment of the Chairman and other members of the UPSC is made by the President of India. Each member of the UPSC serves a term of six years or until reaching the age of 65, whichever comes first. Reappointment is not permitted for individuals who have previously held a position within a Public Service Commission. Members have the option to resign from their office by submitting a written resignation to the President of India.
Removal Union Public Service Commission
The Chairman or any member of the UPSC can only be dismissed from their position by the President of India. The President has the authority to suspend the Chairman or any member pending a reference to the Supreme Court. Grounds for removal include being declared insolvent, engaging in paid employment outside their official duties during their tenure, or being deemed unfit to continue in office due to mental or physical incapacity, as determined by the President.
Functions of UPSC
- The UPSC conducts examinations for All-India Services, Central Services, and Public Services across various Indian states and Union territories.
- It assists states in designing and implementing combined recruitment schemes for services requiring specific qualifications.
- The UPSC acts in the interests of the State upon request from the Governor, with the consent of the President of India.
- The UPSC must be consulted in matters concerning compensation for legal expenses incurred by civil servants defending themselves in legal proceedings, interim appointments exceeding one year, and personnel management issues.
- The suggestions made by the Union Public Service Commission are advisory in nature and are not binding on the government.
Eligible Appointments After End of Term of Service
- The Chairman of the UPSC is disqualified from further employment within the Government of India or a State government.
- The Chairman of a State Public Service Commission (SPSC) is eligible for appointment as the Chairman or member of the UPSC or SPSC but cannot seek employment elsewhere in the government.
- Other members of the UPSC, excluding the Chairman, can be appointed as the Chairman of the UPSC or SPSC but are barred from other government employment.
- Similarly, members of the SPSC, excluding the Chairman, can be appointed as the Chairman or member of the UPSC or SPSC but cannot pursue other government employment.
Independence of UPSC
- The Chairman and other members of the UPSC can only be removed based on grounds specified in the constitution.
- The terms of service for the Chairman and members cannot be altered to their detriment after appointment.
- Expenses of the UPSC are covered by the Consolidated Fund of India, eliminating the need for parliamentary approval.
- The Chairman is ineligible for re-employment in the government, even in the same position.
- While members can be re-appointed to the UPSC or any State PSC, they cannot seek employment elsewhere in the government.
Read about Election Commission and State Public Service Commission.
